beliefs, and seeing that this is the Information Age, what all is/has
changed?
articles posted.
Can a New Supercomputer Beat Jeopardy!'s Best?
Meet Watson: a computer with artificial intelligence capable of
understanding the nuances in human speech. Watson is so smart - and so
knowledgeable about humanity - that it is going to take on the grand
champions of Jeopardy, America's favorite quiz show.
Watson, named after IBM's founder, Thomas J. Watson, is an artificial intelligence program developed by IBM designed to answer questions posed in natural language. It is being developed as part of the DeepQA research project.[1] The program is in the final stages of completion and will run on a POWER7 processor-based system. It is scheduled to compete on the television quiz show Jeopardy! as a test of its abilities; the competition will be aired in three Jeopardy! episodes running from February 14–16, 2011. Watson will compete against Brad Rutter, the current biggest all-time money winner on Jeopardy!, and Ken Jennings, the record holder for the longest championship streak.[
"Watson doesn't have emotions, but it knows of emotions," IBM senior
vice president and director of research Doctor John Kelly III said with a
smile.
At the end of the practice round, Watson had answered most of the
questions correct and was leading with $4,400 against his two
competitors. However, Jennings was close behind at $3400 (and had only
answered one less question correct than Watson), and Rutter was trailing
with $1200. But in Jeopardy, when things can change easily with a Daily
Double, with Final Jeopardy or with simple bad luck by getting a
category you don't know, it's still anyone's or anythings game. Sure
enough, a feed of another practice round following the press conference
showed Ken Jennings leading the competition with Watson not that far
behind.
More at TIME.com:
Can a New Supercomputer Beat Jeopardy!'s Best?
Alex Meets Auto-Tune: Jeopardy's Host Goes Electronica
Techland Interview: Alex Trebek
Read more: https://techland.time.com/2011/01/14/jeopardy-computer-pits-ai-skills-against-humanity/#ixzz1D7YE1NAm
External links
- Watson homepage
- DeepQA homepage
- About Watson on Jeopardy.com
- NOVA: Smartest Machine on Earth
- POWER7
- Power 750
- Power Systems
Evolution
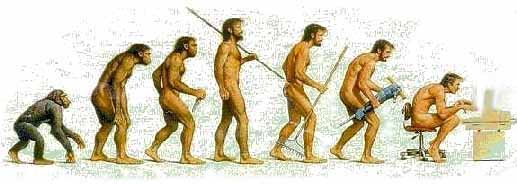
The Theory of Evolution states that modern man evolved from the ape
family. This can not be verified as the 'missing link' has not as yet
been found. There is no conclusive evidence to prove that man evolved
from apes. Footprints of modern man have been found side by side with
dinosaur tracks. Archeological evidence exists that contradicts this
theory of 'the origin of man'. Modern human artifacts have been found
in all layers of geological strata some going back hundreds of millions
of years. These artifacts prove that modern man may be million of years
older than history tells us. Paleontology
In biology, evolution is the change in the heritable traits of a
population over successive generations, as determined by the shifting
allele frequencies of genes. Evolution is ultimately the source of the
vast diversity of life: all contemporary organisms are related to each
other through common descent, products of cumulative evolutionary
changes over billions of years. Over time, new species evolve from
existing species through speciation, and other species become extinct,
resulting in the ever-changing biological world reflected in the fossil
record.
The basic mechanisms that produce evolutionary change are natural
selection (which includes ecological and sexual selection) and genetic
drift acting on the genetic variation created by mutation, genetic
recombination and gene flow. Natural selection is the process by which
individual organisms with favorable traits are more likely to survive
and reproduce. If those traits are heritable, they pass them to their
offspring, with the result that beneficial heritable traits become more
common in the next generation. Given enough time, this passive process
can result in varied adaptations to changing environmental conditions.
The modern understanding of evolution is based on the theory of natural
selection, which was first set out in a joint 1858 paper by Charles
Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace and popularized in Darwin's 1859 book The Origin of Species.
In the 1930s, scientists combined Darwinian natural selection with the
theory of Mendelian heredity to form the modern evolutionary synthesis,
also known as "Neo-Darwinism". The modern synthesis describes evolution
as a change in the frequency of alleles within a population from one
generation to the next. This theory has become the central organizing
principle of modern biology, relating directly to topics such as the
origin of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, eusociality in insects, and
the staggering biodiversity of the living world.
Because of its potential implications for the origins of humankind,
evolutionary theory has been at the center of many social and religious
controversies since its inception.
Continued Wikipedia
In the News ...
New Statistical Model Moves Human Evolution Back Three Million Years Science Daily - November 6, 2010
Evolutionary divergence of humans and chimpanzees likely occurred some 8
million years ago rather than the 5 million year estimate widely
accepted by scientists, a new statistical model suggests.
How plants drove animals to the land PhysOrg - September 30, 2010
A new study of ancient oxygen levels presents the first concrete
evidence that after aquatic plants evolved and boosted the levels of
oxygen aquatic life exploded, leading to fierce competition that
eventually led some fish to try to survive on land.
Animal- Human Connection: Crucial in Human Evolution Science Daily - July 21, 2010
New hypothesis for human evolution and human nature PhysOrg - July 21, 2010
... the interdependency of ancestral humans with other animal species -
"the animal connection" - played a crucial and beneficial role in human
evolution over the last 2.6 million years.
 South African fossils could be new hominid species BBC - April 9, 2010
South African fossils could be new hominid species BBC - April 9, 2010 The remarkable remains of two ancient human-like creatures (hominids) have been found in South Africa.
"Key" Human Ancestor Found: Fossils Link Apes, First Humans? National Geographic - April 8, 2010

An Australopithecus sediba skull bears both human and ape traits.
New species of early hominid found PhysOrg - April 6, 2010

Scientists reveal driving force behind evolution PhysOrg - February 25, 2010
Intelligent people have 'unnatural' preferences and values that are novel in human evolution PhysOrg - February 25, 2010
DNA evidence tells 'global story' of human history PhysOrg - February 22, 2010
Cultural views of evolution can have important ethical implications PhysOrg - February 21, 2010
Evolution may take giant leaps PhysOrg - December 12, 2009
A new study of thousands of species of plants and animals suggests new
species may arise from rare events instead of through an accumulation of
small changes made in response to changes in the environment.
Feeding birds 'changes evolution' BBC - December 3, 2009
Mammoth dung unravels extinction BBC - November 19, 2009
The Future of Evolution: What Will We Become? Live Science - November 16, 2009
Reproduction: Why Having A Mate Provides An Evolutionary Advantage Over Self-fertilization Science Daily - October 22, 2009
The first men and women from the Canary Islands were Berbers PhysOrg - October 21, 2009
Are humans still evolving? Absolutely, says new analysis of long-term survey of human health PhysOrg - October 19, 2009
Time in a bottle: Scientists watch evolution unfold PhysOrg - October 18, 2009
"Darwin's Wing" Fills Evolution Gap National Geographic - October 14, 2009

Ratchet-like genetic mutations make evolution irreversible PhysOrg - September 24, 2009
Evolution Can't Go Backward Live Science - September 24, 2009
Research team finds first evolutionary branching for bilateral animals PhysOrg - September 23, 2009
Three human genes evolved from junk New Scientist - September 3, 2009
New Understanding of the Heart's Evolution Live Science - September 3, 2009
First genetic link between reptile and human heart evolution PhysOrg - September 2, 2009
Why Did People Become White? Live Science - September 2, 2009
Humans Walked After Tree-Climbing Era, Study Indicates Live Science - August 10, 2009
Extinct Walking Bat Found; Upends Evolutionary Theory National Geographic - August 10, 2009
Mobile DNA elements in woolly mammoth genome give new clues to mammalian evolution PhysOrg - June 8, 2009
"Human"-Faced Missing Link Found in Spain? National Geographic - June 11, 2009

An 11.9-million-year-old fossil ape species with an unusually flat, "surprisingly human" face has been found in Spain.
 Scientists hail stunning fossil of a 47-million-year-old, lemur-like creature BBC - May 19, 2009
Scientists hail stunning fossil of a 47-million-year-old, lemur-like creature BBC - May 19, 2009  Ida ... 'Missing link' primate likely to stir debate MSNBC - May 19, 2009
Ida ... 'Missing link' primate likely to stir debate MSNBC - May 19, 2009 Blog: Myth of the Missing Link Live Science - May 20, 2009
Blog: Why 'Ida' Inspires Navel-Gazing at Our Ancestry Live Science - May 20, 2009
Ancient Human Ancestor 'Ida' Discovered - Missing Link? Live Science - May 19, 2009
New Fossil Primate Links Humans, Lemurs? National Geographic - May 19, 2009

Common Ancestor Of Humans, Modern Primates? 'Extraordinary' Fossil Is 47 Million Years Old Science Daily - May 19, 2009
In what could prove to be a landmark discovery, a leading paleontologist
said scientists have dug up the 47 million-year-old fossil of an
ancient primate whose features suggest it could be the common ancestor
of all later monkeys, apes and humans.
Ten fossils that evolved the tale of our origins MSNBC - October 17, 2008
Details Of Evolutionary Transition From Fish To Land Animals Revealed Science Daily - October 16, 2008
Ten fossils that evolved the tale of our origins MSNBC - October 17, 2008
Fish With First Neck Evolved Into Land Animal -- Slowly National Geographic - October 15, 2008
Details Of Evolutionary Transition From Fish To Land Animals Revealed Science Daily - October 16, 2008

Evolutionary Origin Of Mammalian Gene Regulation Is Over 150 Million Years Old Science Daily - July 3, 2008
'Mitochondrial Eve' Research: Humanity Was Genetically Divided For 100,000 Years Science Daily - May 16, 2008
Reason For Almost Two Billion Year Delay In Animal Evolution On Earth Discovered Science Daily - March 27, 2008
Geologists Say 'Wall Of Africa' Allowed Humanity To Emerge Science Daily - December 22, 2007
Mountains of Evidence Suggest Human Evolution Had Rocky Start Live Science - December 20, 2007
Primitive early relative of armadillos helps rewrite evolutionary family tree PhysOrg - December 12, 2007
Human Evolution Speeding Up, Study Says National Geographic - December 11, 2007
Human evolution is 'speeding up' BBC - December 11, 2007
Finds test human origins theory BBC - August 8, 2007
Two hominid fossils discovered in Kenya are challenging a
long-held view of human evolution
Scientists turn to chimpanzees to solve the mystery of our cultural roots MSNBC - August 9, 2007
Greatest Mysteries: How Did Human Culture Evolve? Live Science - August 9, 2007
Kenyan Fossils May Add New Branch to Human Family Tree National Geographic - August 8, 2007
Finds test human origins theory BBC - August 8, 2007
Two hominid fossils discovered in Kenya are
challenging a long-held view of human evolution.
Elephants, Human Ancestors Evolved in Synch, DNA Reveals National Geographic - July 24, 2007
From Jaw to Ear: Transition Fossil Reveals Ear Evolution in Action Scientific American - March 15, 2007
No sex for 40 million years? No problem EurekAlert - March 19, 2007
Surprising Pace of Evolution and Extinction Revealed Live Science - March 16, 2007
Species evolve faster in cooler climates New Scientist - March 16, 2007
Interspecies Sex: Evolution's Hidden Secret? National Geographic - March 15, 2007
Robo-salamander's evolution clues BBC - March 9, 2007
A robot is being used to investigate how the first land animals on Earth might have walked
Evolution Getting Faster Thanks to Germs, Viruses, Study Says National Geographic - March 7, 2007
Researchers Study Formation Of Chemical Precursors to Life PhysOrg - August 7, 2006

Evolution Reversed in Mice BBC - August 7, 2006
US researchers have taken a mouse back in time some 500
million years by reversing the process of evolution.
Fossil Fish With "Limbs" Is Missing Link, Study Says National Geographic - April 6, 2006
Arctic fossils mark move to land BBC - April 5, 2006


Fossil animals found in Arctic Canada provide a snapshot of fish
evolving into land animals, scientists say. The finds are giving
researchers a fascinating insight into this key stage in the evolution
of life on Earth.
Ancient skull found in Ethiopia BBC - March 27, 2006

Fossil hunters in Ethiopia have unearthed an ancient skull which they
say could be a "missing link" between Homo erectus and modern people.
Evolution Predictable Everywhere in the Universe, Scientist Says Live Science - March 14, 2006

Human Genome Shows Proof of Recent Evolution, Survey Finds National Geographic - March 8, 2006

Most Ashkenazi Jews From Four Women Live Science - January 13, 2006
Some 3.5 million of today's Ashkenazi Jews - about 40 percent of the
total Ashkenazi population - are descended from just four women, a
genetic study indicates.
Evolution Revolution: Two Species Become One National Geographic - July 27, 2005
Butterfly unlocks evolution secret BBC - July 24, 2005

Human evolution at the crossroads MSNBC - May 2, 2005
Genetics, cybernetics complicate forecast for species

Scientists Find Portal To Show Animals Evolve Science Daily - February 2005
Earliest Bilateral Fossil Discovered Astrobiology - June 2004

Scientists have reported that bilateral animals appeared 600 million
years ago, about 50 million years before the Cambrian Explosion. Before
the Cambrian 550 million years ago, most life on Earth was composed of
bacteria and single-celled animals. But then something happened to cause
an "explosion" of complex multi-cellular body forms. Scientists have
long been puzzled about why this burst of diversity occurred. Some have
suggested that a sudden rise in oxygen allowed larger and more complex
life forms to appear and develop. Others have suggested that animal
complexity started long before the Cambrian, and that we had only failed
to find fossil evidence of it.
Prehistoric DNA to Help Solve Human-Evolution Mysteries? National Geographic - March 2004
Evolution's Twist: USC Study Finds Meat-tolerant Genes Offset High Cholesterol And Disease Science Daily - March 2004
Snake Ancestors Lost Limbs on Land, Study Says National Geographic - February 2004
Availability of Oxygen Triggered The Evolution Of Complex Life Forms Space Daily - February 2004
Cave colours reveal mental leap BBC - December 2003
Red-stained bones dug up in a cave in Israel are prompting researchers to
speculate that symbolic thought emerged much earlier than they had believed.
Symbolic thought - the ability to let one thing represent another - was a giant leap
in human evolution. It was a mental ability that allowed sophisticated language and maths.
Scientists Find Evolution Of Life Helped Keep Earth Habitable Science Daily - October 2003
Worms hold 'eternal life' secret BBC - October 2003

Key human chromosome unravelled BBC - October 2003

Ancient organism challenges cell evolution BBC - June 2003
Scientists have found an organelle - an enclosed free-floating
specialised structure - inside a primitive cell for the first time.
Darwin Proved Right by Experiment with 'Alien' Life - Survival of the Fittest Space.com - May 2003
Chimps genetically close to humans BBC - May 2003
The creativity gene that maketh man BBC - February 2003
A single mutation in a "creativity" gene less than 100,000 years ago
led to the rapid development of art and culture and the ascent of Man
All humans are descended from a single man who lived in Africa around 60,000 years ago National Geographic - February 2003 -
1.8 Million-Year-Old Hominid Jaw Found National Geographic - February 2003


Fossil find stirs human debate BBC - February 2003
The fossil of an early human-like creature (hominid) from
southern Africa is raising fresh questions about our origins.
Documentary Redraws Humans' Family Tree January 2003 - National Geographic
By analyzing DNA from people in all regions of the world, geneticist
Spencer Wells has concluded that all humans alive today are descended
from a single man who lived in Africa around 6,000 years ago
13,000 year old Human skulls are 'oldest Americans' BBC - December 2002

Life 'began on the ocean floor' BBC - December 2002

Atlas maps the web of life BBC - August 2002
Origin Of Bipedalism Tied To Environmental Changes May 2002 - Science Daily
Videos
- IBM and the Jeopardy Challenge (3:59), IBM
- IBM "Watson" System to Challenge Humans at Jeopardy! (2:29), IBMLabs
- Building Watson – A Brief Overview of the DeepQA Project (21:42), IBMLabs
Accumulated list from www.crystalinks.com...thanks



